Forum breadcrumbs - You are here:CommunityStartup Marketing: How To (All About Startup Marketing)Trusted by experts, available to …
Trusted by experts, available to all
Guest
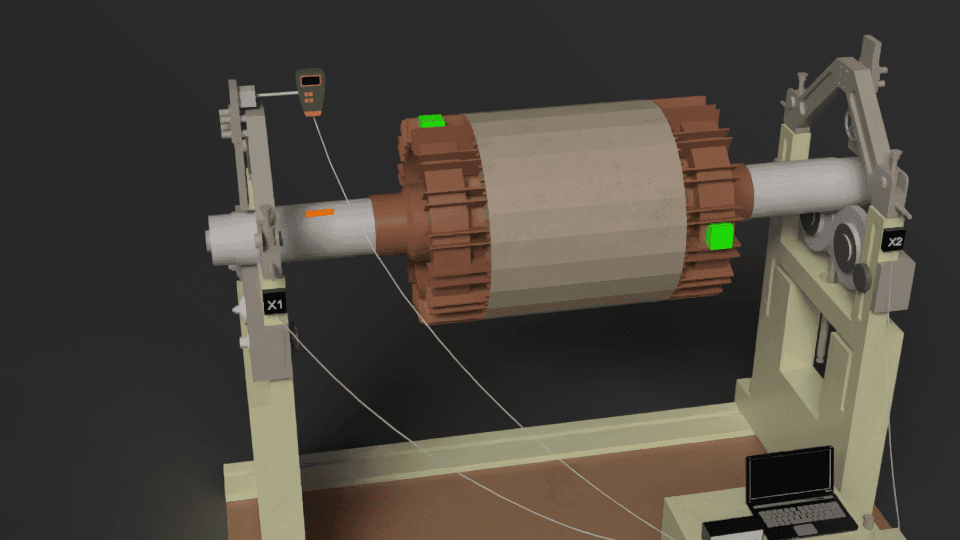
Quote from Guest on December 7, 2024, 10:41 pmUsing the Balanset-1A Instrument
Preparing the Necessary Tools
- vibration sensors, optical speed sensor, magnetic base, software package, and included accessories.
- Connect the device to your PC using the USB interface and confirm the software installation.
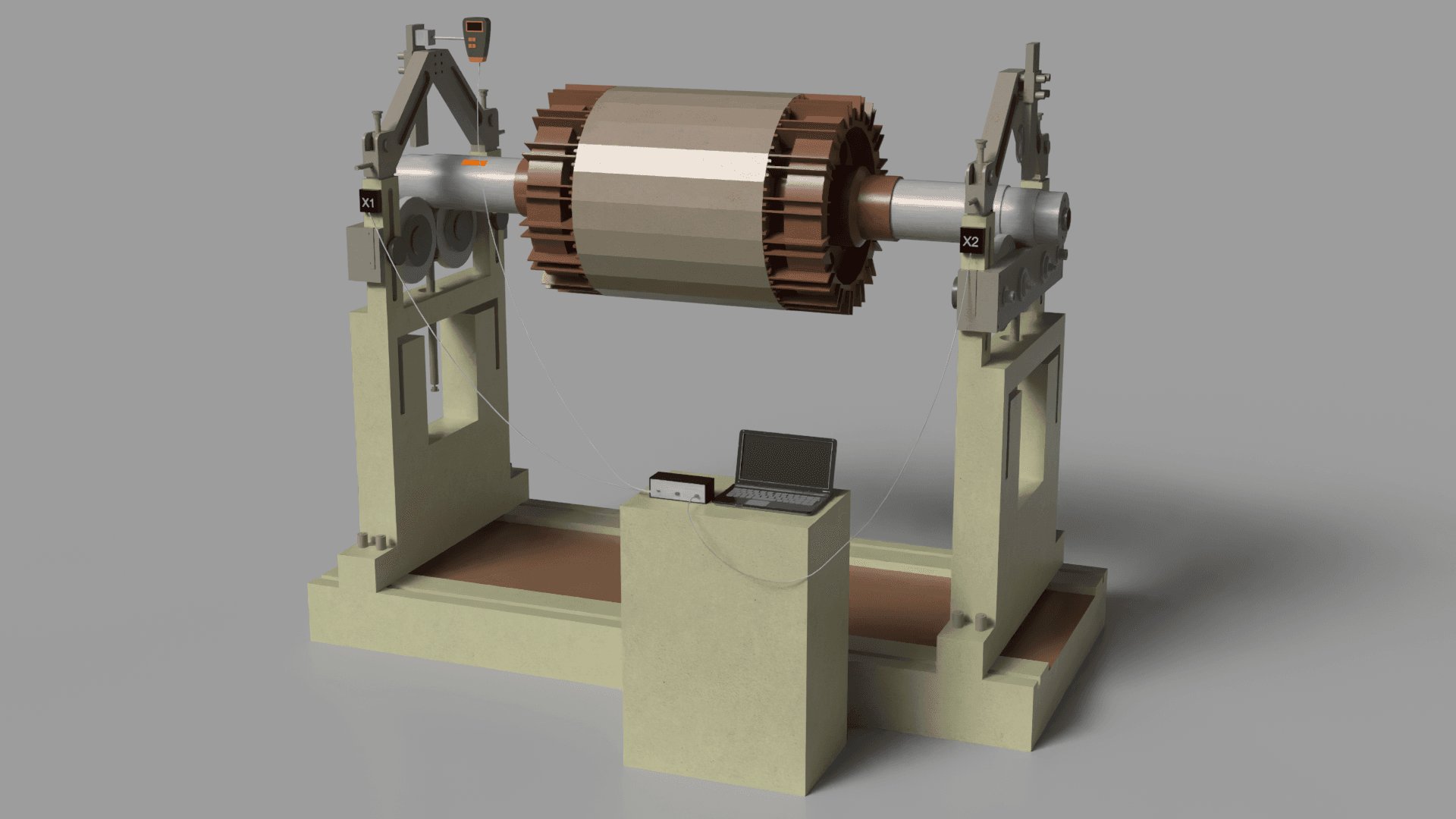
Setting Up the Sensors
- Fix the accelerometers securely to the machine's structure in locations where vibrations are most prominent, ideally near the bearings.
- Direct the laser speed sensor towards the rotor and affix reflective tape to the rotor surface to facilitate phase angle measurement.
Launching the Software
- Launch the Balanset software on your computer.
- Choose the correct balancing method (single or two-plane) according to the rotor configuration and the balancing task.
Taking Baseline Vibration Readings
- Bring the rotor to its normal operating rotational frequency.
- The software will measure the vibration level, rotational speed, and phase angle. This data establishes the current imbalance condition.
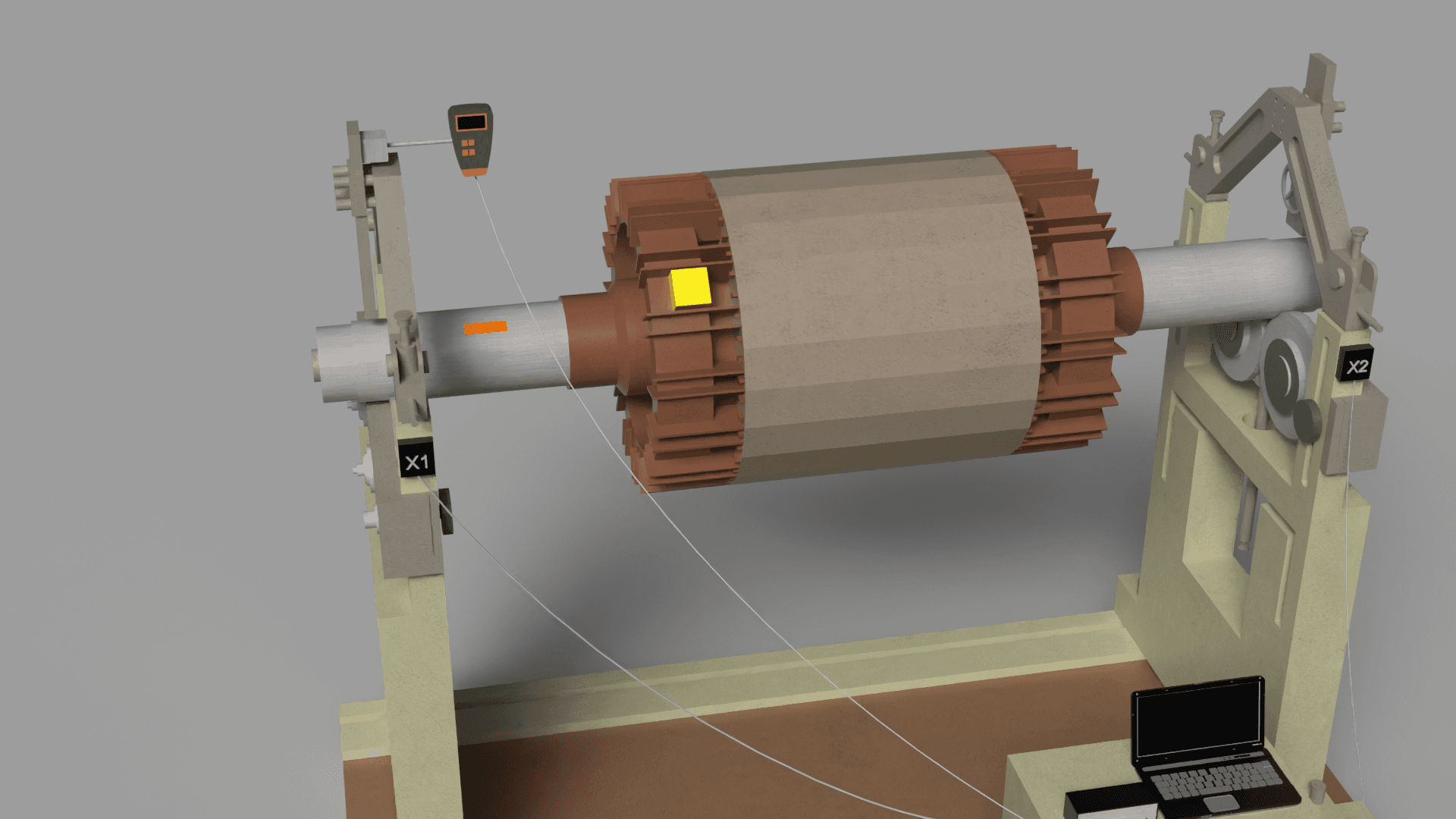
Trial Weight Installation
- Stop the rotor and attach a trial weight at a specific location on the rotor. The weight's mass can be specified within the software (e.g., in grams).
- Restart the rotor, and the software will record the changes in vibration level and phase angle.
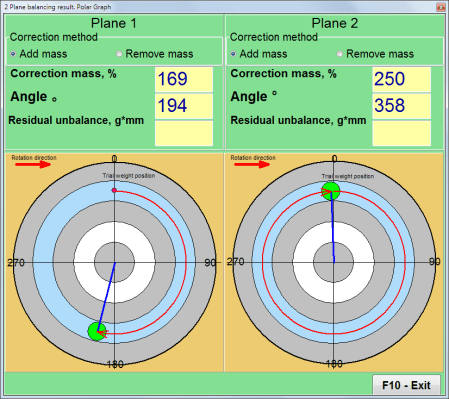
Computing the Compensating Weight
- Using the acquired measurements, the program automatically determines the required corrective weight's mass and angular position.
- The calculated values are presented on-screen in both numerical and graphical formats.
Mounting the Compensating Weight
- Attach the computed compensating weight to the rotor as indicated by the software's output.
- If necessary, perform intermediate checks to verify that the imbalance is being reduced.
Verification and Balancing Completion
- After installing the correction weight, run the rotor again and check the residual vibration level.
- If the measured vibration falls within the tolerance defined by ISO 1940, the balancing process is considered successful.
- If the vibration is still outside acceptable limits, reiterate the process and fine-tune the compensating weight.
Generating a Documentation of the Balancing Results
- The balancing results are saved in the software's archive. You can create and print a report containing vibration data, correction weight mass, and its installation angle.
Post-Balancing Checklist
- Double-check that all weights and sensors are securely fastened.
- Confirm that the rotor spins freely and quietly, without any unusual sounds or vibrations.
- If the rotor is part of a complex mechanism, verify the proper interaction of all its components.
By implementing this method, you can effectively eliminate imbalance, reduce vibration levels, and increase the lifespan of the machinery.
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/vibromera_ou/
Youtube : https://youtu.be/guA6XJ-ArZM?si=vmkuX7RILzKBl0zL
Our website about Balancing of milling machine rotors in tool manufacturing
Using the Balanset-1A Instrument
Preparing the Necessary Tools
- vibration sensors, optical speed sensor, magnetic base, software package, and included accessories.
- Connect the device to your PC using the USB interface and confirm the software installation.
Setting Up the Sensors
- Fix the accelerometers securely to the machine's structure in locations where vibrations are most prominent, ideally near the bearings.
- Direct the laser speed sensor towards the rotor and affix reflective tape to the rotor surface to facilitate phase angle measurement.
Launching the Software
- Launch the Balanset software on your computer.
- Choose the correct balancing method (single or two-plane) according to the rotor configuration and the balancing task.
Taking Baseline Vibration Readings
- Bring the rotor to its normal operating rotational frequency.
- The software will measure the vibration level, rotational speed, and phase angle. This data establishes the current imbalance condition.
Trial Weight Installation
- Stop the rotor and attach a trial weight at a specific location on the rotor. The weight's mass can be specified within the software (e.g., in grams).
- Restart the rotor, and the software will record the changes in vibration level and phase angle.
Computing the Compensating Weight
- Using the acquired measurements, the program automatically determines the required corrective weight's mass and angular position.
- The calculated values are presented on-screen in both numerical and graphical formats.
Mounting the Compensating Weight
- Attach the computed compensating weight to the rotor as indicated by the software's output.
- If necessary, perform intermediate checks to verify that the imbalance is being reduced.
Verification and Balancing Completion
- After installing the correction weight, run the rotor again and check the residual vibration level.
- If the measured vibration falls within the tolerance defined by ISO 1940, the balancing process is considered successful.
- If the vibration is still outside acceptable limits, reiterate the process and fine-tune the compensating weight.
Generating a Documentation of the Balancing Results
- The balancing results are saved in the software's archive. You can create and print a report containing vibration data, correction weight mass, and its installation angle.
Post-Balancing Checklist
- Double-check that all weights and sensors are securely fastened.
- Confirm that the rotor spins freely and quietly, without any unusual sounds or vibrations.
- If the rotor is part of a complex mechanism, verify the proper interaction of all its components.
By implementing this method, you can effectively eliminate imbalance, reduce vibration levels, and increase the lifespan of the machinery.
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/vibromera_ou/
Youtube : https://youtu.be/guA6XJ-ArZM?si=vmkuX7RILzKBl0zL
Our website about Balancing of milling machine rotors in tool manufacturing
Click for thumbs down.0Click for thumbs up.0